E3 model
Trade-off Analysis Euros, Energy & Emissions.
With the E3 model, we use a life cycle approach that includes the financial impact, energy savings and climate impact of sustainable measures.
E3 Model
The E3 model provides insight into the impact of sustainability measures and helps make data-driven choices. We map the financial impact, energy savings and environmental burden through a life cycle assessment (LCA) for environmental impact and a life cycle cost analysis (LCC) for costs. Based on these insights, a clear picture of the most attractive sustainable measures is created.
For the LCA, we analyze:
- Avoided CO2-emissions due to energy reduction.
- Environmental burden of materials used.
- Material burden of maintenance and replacement.
- Circularity of materials used.
For the LCC, we analyze:
- Initial investment.
- Cost savings due to energy reduction.
- Cost of maintenance and replacement.
- Residual value.
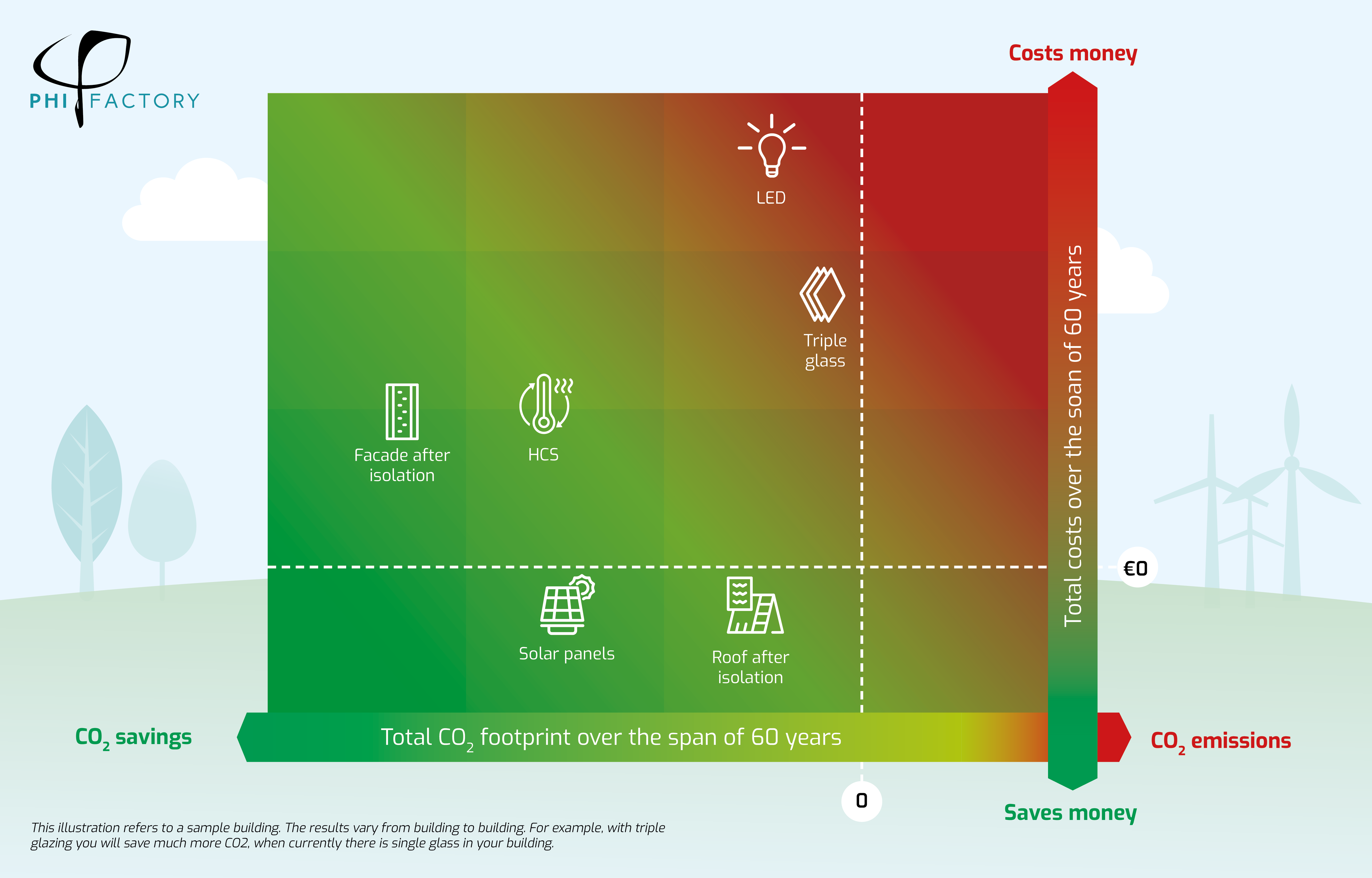
Figure: The E3 model makes choices easy: facade insulation in this case has both the most avoided emissions and the lowest (even negative) life cycle cost. Over its lifetime, therefore, it makes a profit. Then the choice goes between Floor insulation and PV panels: one scores better on climate, the other on cost, but both are more attractive than LED lighting.

Design
How do I design a new building to be as sustainable as possible? Using variant studies, we help provide insight into the CO2 and financial impact of design choices. In doing so, we include the materialization of the entire building and look at the entire life cycle.

Sustainability plan/roadmap
Making your building more sustainable can be done in many ways, but sometimes you have to make choices within the available budget. Do we put PV panels on the roof or do we insulate? And which insulating materials have the lowest environmental impact. We make the choice easy by looking at the entire life cycle from both a climate and financial perspective. Here we can examine different scenarios: What achieves the greatest impact? What is possible within the available budget? Which measures are the most cost-effective?
Material choice
There are numerous routes to a sustainable building. That is why it is important to calculate the measures in terms of the intended energy savings as well as the environmental impact of the materials. Suppose you want to insulate the facade: what material should be used? How does the Rd value of the insulation material compare to the CO2 footprint of the material? Things like environmental burden, lifespan, maintenance and residual value all affect the effectiveness of the measure. With the E3 model, we put different options side by side to make a data-driven choice.
Praktijkverhalen
More information?
Our expert will happily tell you more.



